What is GRC? Understanding Governance, Risk, and Compliance
In the complex world of modern business, maintaining a strong, cohesive framework for managing governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) is critical. Organizations face a multitude of challenges that span across regulatory requirements, ethical practices, operational risks, and strategic objectives. These challenges require a unified approach to ensure long-term success, sustainability, and integrity.
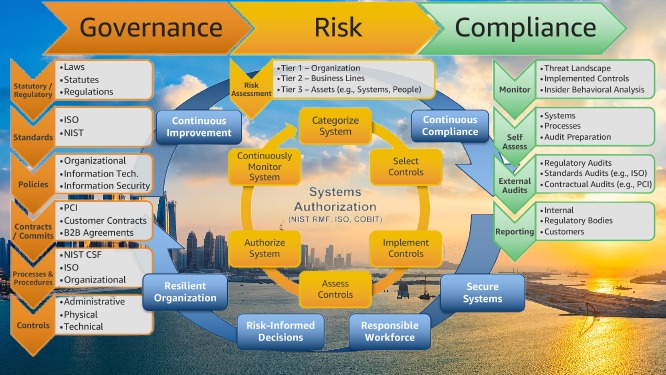
GRC, an acronym for Governance, Risk, and Compliance, is a holistic approach used by organizations to align their business processes with regulatory and legal requirements while managing risks and adhering to internal governance policies. It encompasses three distinct but interconnected elements: governance, risk management, and compliance. Together, these functions help organizations make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and maintain compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the meaning of GRC, its importance, the individual components that make up GRC, its benefits, and how it can be effectively implemented within organizations.
What is GRC?
GRC stands for Governance, Risk, and Compliance. It is a strategic framework that integrates these three crucial components to ensure that an organization can achieve its objectives, manage risks, and remain compliant with laws and regulations, all while maintaining sound corporate governance. The goal of GRC is to create a structured, coordinated, and comprehensive approach to managing an organization’s business practices.
Let’s break down the components of GRC:
Governance: This refers to the frameworks, policies, and processes that guide how an organization is controlled and directed. It encompasses decision-making processes, accountability, leadership structures, and corporate culture. Good governance ensures that the organization operates ethically, efficiently, and in line with its objectives and values.
Risk Management: Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could potentially affect an organization’s ability to achieve its goals. Risks can arise from various sources, including market fluctuations, operational disruptions, cyber threats, and regulatory changes. Effective risk management ensures that organizations are prepared to handle uncertainties, minimizing potential negative impacts on their operations.
Compliance: Compliance refers to adhering to legal, regulatory, and ethical standards that apply to an organization’s industry and operational activities. This involves following internal policies and external regulations, such as data protection laws, financial reporting standards, and health and safety regulations. Failure to comply with these rules can result in legal penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses.
Together, these three elements work to promote a unified and proactive approach to risk mitigation, regulatory adherence, and ethical business practices.
The Evolution of GRC

The concept of GRC (governance risk management and compliance in Delhi) has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Traditionally, governance, risk management, and compliance were treated as separate functions within organizations. This siloed approach often led to inefficiencies, redundancies, and a lack of coordination between departments. As a result, organizations struggled to manage their risks effectively, often encountering challenges such as conflicting priorities, inconsistent risk assessments, and fragmented compliance processes.
The need for a more integrated approach became apparent in the early 2000s, particularly after major corporate scandals such as the Enron and WorldCom debacles, which highlighted the importance of strong corporate governance and robust risk management practices. The introduction of regulatory frameworks such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) in the United States further emphasized the need for better internal controls and reporting mechanisms.
GRC emerged as a response to these growing challenges, providing organizations with a structured framework for managing governance, risk, and compliance in a coordinated manner. Over time, GRC has evolved to incorporate advanced technologies, such as automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, to streamline processes and enhance decision-making.
Key Components of GRC
Understanding the individual components of GRC is essential for grasping how the entire framework operates. Below, we explore each component in detail:
Governance
Governance is the cornerstone of GRC, as it establishes the rules, policies, and structures that guide how an organization is managed and operated. It involves setting clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability for decision-making across all levels of the organization. Governance also defines the ethical standards and corporate culture that shape the organization’s behaviour and ensure that all actions align with its mission and values.
Effective governance is characterized by the following elements:
Board and Leadership Oversight: The board of directors and executive leadership play a critical role in governance by providing strategic direction, approving major decisions, and ensuring accountability throughout the organization.
Internal Controls: Governance includes establishing internal controls that safeguard assets, ensure the integrity of financial reporting, and promote operational efficiency.
Corporate Culture: The organization’s culture should reflect its commitment to ethical behavior, transparency, and accountability. Strong governance fosters a positive corporate culture that encourages ethical decision-making and responsible business practices.
Stakeholder Engagement: Good governance involves considering the interests of various stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, and the community. This ensures that decisions are made with a broad perspective in mind, promoting long-term value creation
Risk Management
Risk management is a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to potential risks that could affect the organization’s ability to achieve its objectives. Risks can come from a variety of sources, including financial markets, operational inefficiencies, legal and regulatory changes, cybersecurity threats, and environmental factors.
Key elements of risk management include:
Risk Identification: This involves identifying potential risks that could impact the organization, including strategic, operational, financial, and reputational risks.
Risk Assessment: Once risks are identified, they must be assessed in terms of their likelihood and potential impact. This allows organizations to prioritize risks and allocate resources accordingly.
Risk Mitigation: After assessing risks, organizations can implement measures to mitigate or manage them. This may involve transferring risks through insurance, reducing risks by implementing internal controls, or accepting risks that are deemed tolerable.
Monitoring and Review: Risk management is an ongoing process, and risks must be continually monitored and reviewed to ensure that mitigation strategies remain effective.
Risk management is crucial for maintaining business continuity and protecting the organization from unforeseen challenges that could derail its operations
Compliance
Compliance refers to adhering to legal and regulatory requirements, as well as internal policies and industry standards. It ensures that the organization operates within the boundaries of the law and maintains ethical business practices.
Compliance involves the following elements:
Regulatory Compliance: Organizations must comply with industry-specific regulations and laws, such as data protection laws (e.g., GDPR), financial reporting requirements, and environmental regulations.
Internal Compliance: In addition to external regulations, organizations must also comply with internal policies and codes of conduct that govern employee behaviour, financial practices, and operational processes.
Monitoring and Auditing: Compliance requires ongoing monitoring and auditing to ensure that all activities adhere to legal and regulatory requirements. Regular audits help identify potential compliance gaps and areas for improvement.
Training and Education: Employees must be trained on relevant compliance requirements to ensure that they understand the laws and regulations that apply to their roles. This helps create a culture of compliance throughout the organization.
Non-compliance can result in severe consequences, including legal penalties, financial losses, and reputational damage. Therefore, maintaining a robust compliance framework is critical to the organization’s success.
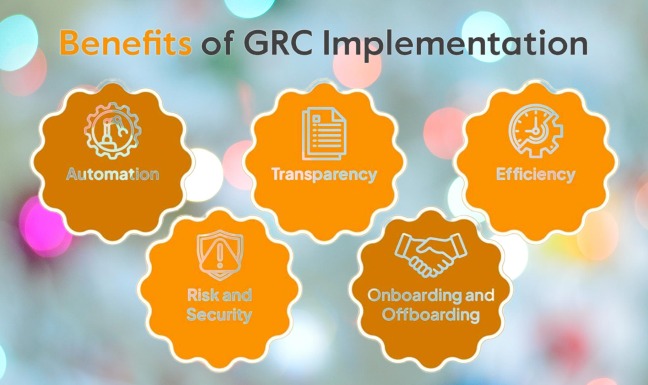
The Benefits of Implementing GRC
Implementing a comprehensive GRC framework offers numerous benefits to organizations:
Improved Decision-Making
By integrating governance, risk management, and compliance into a unified framework, organizations can make more informed decisions. GRC provides a holistic view of the organization’s risk landscape, allowing leaders to consider potential risks and regulatory implications when making strategic decisions.
Enhanced Efficiency
GRC eliminates silos by promoting collaboration between departments responsible for governance, risk management, and compliance. This streamlines processes, reduces redundancies, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Risk Mitigation
A robust GRC framework enables organizations to proactively identify and mitigate risks before they materialize. By continuously monitoring the risk environment, organizations can respond to emerging threats in real time, minimizing potential disruptions to their operations.
Regulatory Compliance
GRC ensures that organizations remain compliant with industry regulations and legal requirements. This helps avoid costly fines, legal disputes, and reputational damage that can result from non-compliance.
Increased Accountability
With clear governance structures in place, GRC promotes accountability at all levels of the organization. Employees understand their roles and responsibilities, and there is greater transparency in decision-making and risk management processes.
Reputation Management
Organizations with a strong GRC framework are better equipped to manage reputational risks. By adhering to ethical standards and maintaining compliance, organizations can build trust with stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulatory bodies.
Implementing a GRC Framework
Successfully implementing a GRC framework requires careful planning and coordination. Here are the key steps involved in implementing GRC within an organization:
Assess Current Practices
The first step in implementing GRC is to assess the organization’s current governance, risk management, and compliance practices. This involves identifying existing gaps and areas for improvement. Conducting a thorough audit of current processes, policies, and systems will provide a baseline for developing the GRC framework.
Define GRC Objectives
Organizations should clearly define their GRC objectives and how they align with overall business goals. This involves setting measurable targets for governance, risk management, and compliance efforts.
Develop Policies and Procedures
The next step is to develop policies and procedures that govern how GRC will be managed. This includes creating governance structures, risk management protocols, and compliance guidelines that are tailored to the organization’s specific needs.
Implement Technology Solutions
GRC technology platforms can help automate key processes, such as risk assessments, compliance monitoring, and reporting. Implementing the right technology solutions can streamline GRC efforts, improve data visibility, and enhance decision-making.
Train Employees
Training employees on GRC policies and procedures is essential to creating a culture of governance, risk awareness, and compliance. Regular training sessions and workshops ensure that employees understand their roles in maintaining GRC standards.
Monitor and Review
GRC is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and review. Organizations should regularly assess the effectiveness of their GRC framework and make adjustments as needed to address new risks or regulatory changes.
Conclusion

GRC—governance, risk, and compliance—is a comprehensive framework that helps organizations align their business practices with legal and regulatory requirements, manage risks, and maintain ethical standards. By integrating these three components, organizations can enhance their decision-making, mitigate risks, and remain compliant with industry regulations. The importance of GRC cannot be overstated in today’s fast-paced, highly regulated business environment. Organizations like ACATL that implement a robust GRC (governance, risk management and compliance in Delhi) framework are better positioned to navigate challenges, protect their reputations, and achieve long-term success.
10 FAQs on “What is GRC? Understanding Governance, Risk, and Compliance”
1. What does GRC stand for?
GRC stands for Governance, Risk, and Compliance, which is a framework that helps organizations align their operations with regulatory requirements, manage risks effectively, and ensure proper governance to achieve their business objectives.
2. What is the purpose of GRC?
The purpose of GRC is to provide an integrated approach to manage an organization’s governance, risk management, and compliance with laws and regulations. It ensures that the organization operates efficiently, minimizes risks, and remains compliant with relevant standards.
3. What is governance in the context of GRC?
Governance refers to the structures, policies, and processes that guide an organization’s decision-making, ensuring accountability, transparency, and ethical behavior. It helps align the organization’s objectives with stakeholder interests.
4. What is risk management in GRC?
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impact the organization’s objectives. It involves recognizing potential threats and implementing strategies to minimize their impact.
5. What is compliance in GRC?
Compliance refers to adhering to laws, regulations, policies, and standards that apply to an organization. It ensures that the organization follows legal and ethical standards to avoid penalties, legal issues, and reputational damage.
6. Why is GRC important for businesses?
GRC is important because it enables organizations to manage risks proactively, ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and implement effective governance practices. This reduces the likelihood of costly penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
7. How does GRC benefit an organization?
GRC benefits organizations by:
Enhancing decision-making with better risk awareness.
Reducing compliance and regulatory risks.
Improving operational efficiency and accountability.
Fostering a culture of ethical behavior and transparency.
Enabling a structured approach to managing risks and compliance.
8. What tools or software are used in GRC?
GRC software platforms help organizations manage governance, risk, and compliance activities more efficiently. Popular GRC tools include MetricStream, RSA Archer, IBM OpenPages, and SAP GRC, which offer features like risk assessment, audit management, and compliance tracking.
9. How does GRC differ from traditional risk management?
Traditional risk management often focuses on specific risks, while GRC takes a holistic approach, integrating governance, risk, and compliance efforts across the entire organization. GRC provides a unified framework to manage multiple risks and regulatory requirements.
10. Who is responsible for implementing GRC in an organization?
GRC is typically a collaborative effort involving senior management, risk managers, compliance officers, internal auditors, and legal teams. The board of directors plays a crucial role in overseeing governance, while operational teams ensure compliance and risk management are embedded in daily activities.