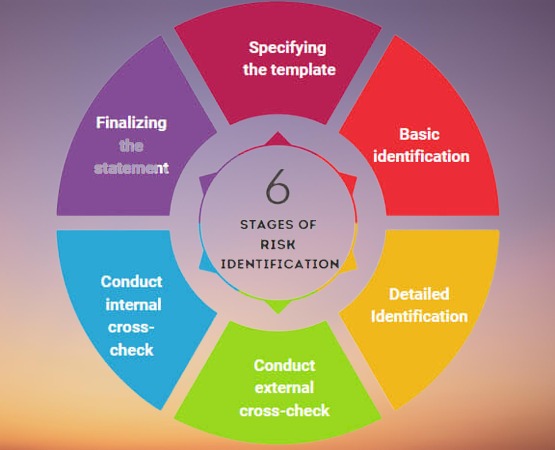
What is the First Step in a Risk Assessment?
Risk assessment is a critical element in the broader process of risk management. It involves identifying, analyzing, and responding to potential risks that could affect an organization’s ability to achieve its objectives. Among the many steps involved in a full risk assessment, the first step is perhaps the most crucial: identifying the risks. Without a comprehensive understanding of what risks are present, it is impossible to assess, mitigate, or manage them effectively.
In this article, we will delve into what the first step in a risk assessment entails, why it is essential, and how businesses can ensure they start their risk assessment processes on the right foot.
The Importance of Risk Identification
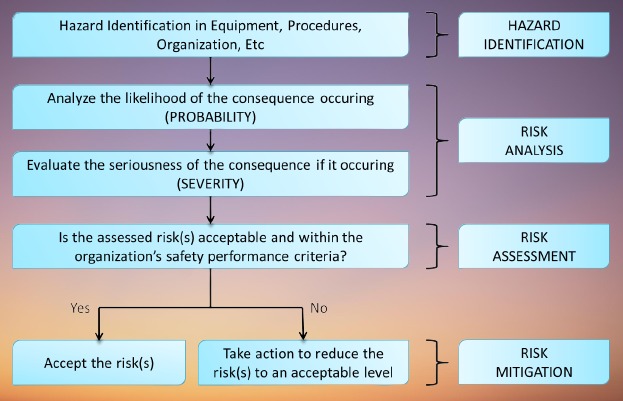

The first step in risk assessment—identifying risks—forms the foundation for everything that follows in the risk management process. If an organization fails to recognize key risks, those risks could go unaddressed, potentially leading to significant negative outcomes such as financial loss, reputational damage, or legal consequences.
This step involves taking a thorough and systematic approach to uncover all potential risks that may impact the organization. Risks can stem from various areas, including internal operations, external market forces, technological advancements, legal and regulatory changes, or environmental factors. A failure to identify risks properly may leave organizations vulnerable to unforeseen threats, often resulting in costly damage control measures.
Methods for Identifying Risks
There are several methods that organizations use to ensure a comprehensive risk identification process:
Internal Consultation and Stakeholder Input: One of the most effective ways to identify risks is by consulting key stakeholders within the organization. This could include senior management, department heads, employees, and any relevant external partners. Each group may have unique insights into potential risks within their specific areas of expertise or responsibility.
Reviewing Historical Data and Past Incidents: Another powerful way to identify risks is to examine historical data. Past incidents—whether financial, operational, or otherwise—can serve as a rich source of information about potential future risks. By reviewing past occurrences and analyzing how they were managed (or mismanaged), organizations can often identify areas that need improvement and where new risks may arise.
Industry Benchmarking: Comparing your business against others in the same industry can help identify risks specific to your field. For example, regulatory risks may affect businesses in highly regulated industries like finance, healthcare, or construction, and benchmarking can reveal common risks that competitors are also dealing with.
Scenario Analysis: This technique involves considering a range of possible future scenarios—both best- and worst-case—and identifying the risks inherent in each. Scenario analysis allows organizations to anticipate not just the obvious risks but also more extreme or unlikely ones, helping to prepare for various contingencies.
SWOT Analysis: A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis helps organizations evaluate internal and external factors that could present risks. This method allows businesses to identify not just their internal weaknesses but also external threats that might not be as readily apparent.
Brainstorming Sessions: Organized brainstorming sessions involving team members from across different departments can help uncover risks that might otherwise be overlooked. Each team member brings a unique perspective, and the collective discussion often reveals potential risks that a single individual might not identify on their own.
Regulatory and Legal Review: Many risks come from changes in laws and regulations. Regularly reviewing legal and regulatory updates helps businesses stay compliant and avoid potential legal risks, such as fines or sanctions.
Categorizing Identified Risks
After identifying potential risks, it is important to categorize them. This helps in organizing the risks and ensuring a more targeted response in subsequent risk management steps. Common categories include:
Operational Risks: These are risks arising from day-to-day business operations, such as supply chain disruptions, equipment failure, or process inefficiencies.
Financial Risks: These risks pertain to financial losses or disruptions, including market volatility, credit risk, or exchange rate fluctuations.
Legal and Compliance Risks: These are risks associated with regulatory changes, legal disputes, or non-compliance with industry standards.
Technological Risks: These risks come from technology failures or cyber threats, such as data breaches or system breakdowns.
Reputational Risks: Negative public perception or damage to a company’s reputation can significantly impact its operations and profitability.
Strategic Risks: These risks arise from poor business decisions or strategies, such as entering an unprofitable market or investing in a failing product.
Risk Identification Tools
To make the identification process efficient, many organizations use specialized tools to help structure and systematize risk identification. Some common tools include:
Risk Registers: A risk register is a document used to record all identified risks in one place. It typically includes details about the source of the risk, its potential impact, likelihood of occurrence, and possible responses.
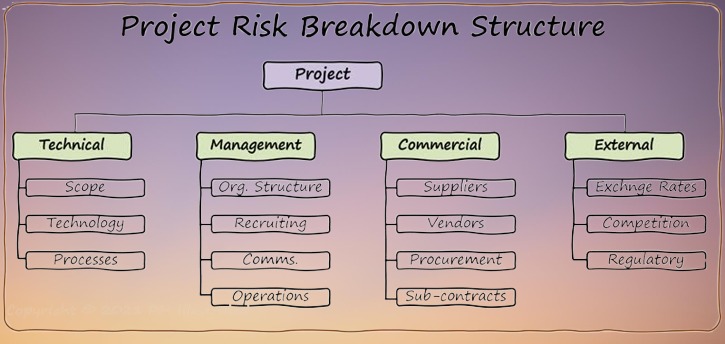
Risk Breakdown Structures (RBS): An RBS is a hierarchical framework that helps categorize risks into broader categories (such as financial, operational, or legal), providing a clearer picture of the types of risks the organization faces.
Risk Matrices: These tools allow businesses to map out risks visually, plotting them based on their likelihood and potential impact. This makes it easier to prioritize the most significant risks.
Best Practices for Effective Risk Identification
While there are many methods and tools available for identifying risks, there are a few key best practices that can help organizations get the most out of this process:
Engage Multiple Perspectives: Risks can affect different parts of the organization in various ways. Engaging a diverse group of stakeholders ensures that a wide range of risks is identified, and no critical area is overlooked.
Make it an Ongoing Process: Risk identification is not a one-time task. As organizations grow, their risk profiles change. New technologies, regulations, and markets can introduce new risks. It’s important to revisit risk identification periodically and integrate it into the overall strategic planning process.
Encourage Open Communication: Encouraging employees at all levels to report risks they encounter is crucial for effective risk identification. Open communication and a culture of transparency enable early detection of risks that might otherwise go unnoticed until it’s too late.
Document All Findings: All identified risks should be thoroughly documented, providing a clear reference point for future steps in the risk assessment process. This documentation can also help in tracking the organization’s risk landscape over time, allowing for better adaptation to new challenges.
Utilize Technology: Risk management software can help automate parts of the risk identification process, making it easier to gather, organize, and track risks across the organization.
Why Risk Identification is the First Step
Risk identification is the first step in a risk assessment because it establishes the groundwork for every subsequent action. Without an accurate and thorough understanding of what risks exist, it is impossible to properly assess their likelihood or impact, and mitigation strategies will likely be ineffective. By focusing on identifying potential risks early, organizations can proactively prepare for and mitigate those risks before they turn into costly problems.
In conclusion, the first step in any risk assessment—risk identification—lays the foundation for an organization’s risk management strategy. Through systematic and comprehensive methods, businesses can ensure they identify all potential threats and vulnerabilities, thus allowing them to create targeted strategies to mitigate those risks effectively. For companies like ACATL, which specialize in corporate legal services in Delhi, an accurate and thorough risk identification process is critical to helping clients navigate the complex and ever-evolving risk landscape in today’s business world.
FAQs on “What is the First Step in a Risk Assessment?
1. What is the first step in a risk assessment?
The first step in a risk assessment is risk identification, which involves identifying potential hazards or risks that could negatively affect the project, business, or organization.
2. Why is risk identification the first step in a risk assessment?
Risk identification is the foundation of the risk assessment process. Without identifying potential risks, it’s impossible to assess or manage them. This step ensures that all possible threats are acknowledged early on to be addressed proactively.
3. What methods are commonly used for identifying risks?
Common methods for identifying risks include brainstorming, checklists, interviews, historical data analysis, and SWOT analysis. These techniques help identify risks from various perspectives, ensuring thorough risk identification.
4. Who is responsible for identifying risks in an organization?
Risk identification is typically a collaborative effort involving various stakeholders. This can include project managers, risk managers, team members, department heads, and external experts, depending on the scope of the risk assessment.
5. What types of risks should be identified in the first step?
In the first step of risk assessment, all potential risks should be considered. This includes financial, operational, legal, environmental, and strategic risks, as well as external factors such as market fluctuations or regulatory changes.
6. How do you document risks during the identification step?
Risks are usually documented in a risk register or a similar log, where each risk is described, and relevant details such as its cause, potential impact, and any associated dependencies are noted for further analysis.
7. What happens if a risk is not identified in the first step?
If a risk is not identified in the first step, it may go unnoticed until it becomes an issue. This can lead to unforeseen challenges that disrupt the business or project and may result in costly or time-consuming mitigation efforts later.
8. What role do employees play in risk identification?
Employees play a crucial role in risk identification, especially those involved in day-to-day operations. Their firsthand experience allows them to recognize potential hazards or inefficiencies that management might overlook.
9. Can new risks be identified after the first step in a risk assessment?
Yes, new risks can emerge throughout the project or operational lifecycle. This is why risk assessment is a dynamic process, and risks should be monitored and reassessed regularly to account for new or evolving threats.
10. What tools or software are useful in the risk identification process?
Tools such as risk assessment templates, risk registers, and specialized software like Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platforms can help streamline the risk identification process by providing frameworks to document and analyze risks.